http://www.malaysiakini.com/news/55854
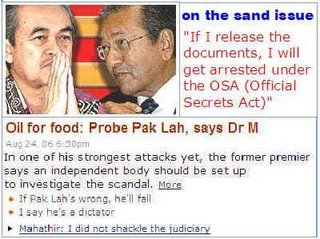
Oil for food: Probe Pak Lah, says Dr M; Aug 24, 06 6:50pm
Dr Mahathir is resorting to “tit-for-tat” in his attack on PM Abdullah
Former premier Dr Mahathir Mohamad said an independent body should be formed to investigate Abdullah Ahmad Badawi's alleged involvement in the United Nations Oil for Food Programme scandal.
In what appeared to be one of his harshest attacks against his handpicked
successor, Mahathir argued that government officials should not be involved
in any commercial transactions.
Responding to a question on the scandal at a press conference in Kedah
yesterday, the former premier said he was only aware of the matter after
stepping down in 2003.
"When I was PM, I was not aware (of this) ... only after I stepped down was
the (UN) report made (public). What is important is not whether he
(Abdullah) is a beneficiary or not but as a deputy prime minister - or
anyone who holds a (government) position - he should not be involved in any
commercial transactions.
"It looks like he was involved. How far he was involved, I don't know ...
but I think there should be an investigation by an independent body, not by
those under him," he said.
Mahathir added that Indian cabinet minister Natwar Singh had resigned when
his name also appeared on the report.
Although two of Abdullah's relatives were implicated in the scandal, the
premier was however later cleared of any involvement by the UN. (see Msiakini report below dated Oct 30 05)
http://www.malaysiakini.com/news/42468
His relatives were identified as Faek Ahmad Shareef, an Iraqi immigrant who
was married to Abdullah's sister-in-law but later divorced, and Noorasiah
Mahmood, the sister of Abdullah's late wife Endon Mahmood.
It was reported that the duo, through a Malaysian trading company called Mastek, were allegedly the biggest bribe-giver to the illicit oil-for-food
deal involving deposed Iraqi leader Saddam Hussein.
Below is an abstract of the press conference, which were published by online
website Agendadaily.
Question: (In reference to Mahathir's decision to attend the Umno general
assembly). Are you planning to speak at the assembly if given the chance?
Mahathir: Yes, if I am allowed to speak, I will speak ... if I am permitted.
* Have you signed the forms to be a delegate (for Umno Kubang Pasu
division)?
Signed already ... signed it early.
* So there's no turning back?
No turning back. I am an ordinary member of Umno - the first member of Umno
(Baru formed following the 1987 crisis). Now, I cannot even talk in Umno.
* Wouldn't your presence lead to a tense situation at the meet?
There shouldn't be any tension. I know that when we have a general assembly, everyone stands up to say 'we support, we support' - not like the Umno during my time. I myself got hammered (at the meets) ... so in Umno, there is freedom of speech but if we have an Umno where everybody says 'we support ', 'we agree', 'we are yes ministers', it no longer looks like Umno. Umno has become something else.
* As a former prime minister, are you going to sit behind (the hall) with the rest of the delegates?
When I was president, I also sat behind to see how it felt. If they don't let me sit in front, I'll sit behind.
* Some consider the current situation stems from your 22 years in power...
What I did ... my era ...everyone could talk. Tunku Abdul Rahman could talk no restrictions. When Tengku Razaleigh (Hamzah) went against me, Abdullah went against me, Musa (Hitam) went against me, there were no restrictions. Now there is completely no freedom and this is what I find strange. Not only the ordinary members cannot talk but even the former president cannot talk either.
(During my era) Tunku Abdul Rahman could talk. Tenglu Razaleigh campaigned
throughout Malaysia, Abdullah Ahmad Badawi campaigned throughout the country
saying I was communist and all; I did not use my powers to stop him.
* So you never blacklisted your critics?
No. In fact, I accepted them back into the cabinet. Rais Yatim burnt all the bridges but came back as a minister. Kadir Sheikh Fadzir, Syed Hamid Albar and even Pak Lah himself - he went against me. I am not a person who blacklists. If you fight for Umno, you have the right (to remain in Umno).
* For 22 years, you never used the words 'I'm prime minister' (which Abdullah mentioned in a recent speech). What is your view on this?
I felt that even being made prime minister, I am actually a servant to the people. So we cannot show so much that as prime minister I can do whatever. That's why I said (in his speech earlier), don't chant 'Hidup Mahathir' ... (chant) Hidup Umno ... Hidup Melayu. What's important are Umno and the Malays, not me ... I am not important.
I'm only expressing the views of those who have told me of their dissatisfaction but live in fear. If they are contractors, they would lose their contracts, if they are government employees then action will be taken against them - all sorts of fears.
There are menteri besar who have been instructed (to do things), but when asked they say 'no, no'... I know this is happening, (they have been) instructed by Khairy (Jamaluddin, the premier's son-in-law).
* The prime minister has ordered the ministers to answer the issues you have raised. They feel that they have answered. What about you?
I asked a simple question - did you offer sand to Singapore, yes or no? No answer. Instead, they tell me to answer. How am I to answer? The documents are with him. If I release the documents, I will get arrested under the OSA (Official Secrets Act).
* But Deputy Prime Minister Najib Abdul Razak said that you can submit the evidence behind closed doors?
(If) closed, I don't want ... let it be open. If it's closed, he will not tell people. I want to bring it out. Give me a declaration that whatever documents I have, I can expose them without any OSA action being taken against me. Give me a written declaration, I will provide the proof.
* If given that assurance, you will expose the evidence?
I will look (for it)...
* People want to know if the evidence is already in your hands?
Why should people want to know? If they know, they will start investigating, search my room (for it)... No need. I know that technique - ransack, ransack.
* There are those who say your actions are aimed at weakening Pak Lah's
position as prime minister and eventually topple him.
If he is only doing the right things, (he) won't fall. If he does wrong, he will fall.
* During your speech, you claimed that two weeks after you stepped down,
those who came to see you were blacklisted. Do you have proof of this?
I was told (they) would be blacklisted.
* Maybe this is just hearsay?
This is why it is difficult when people ask me for proof that I cannot give. I am asking for the proof that he (Abdullah) can give.
* But in today's world, everything requires proof?
I know he has the proof but he is not showing (it). I cannot bring out the (classified) documents or I will get arrested. Secret things he can declassify but he is not doing it. He declassified my letter (to former Singapore premiers Lee Kuan Yew and Goh Chock Tong). My letter was already published by Singapore, so why?
* (Returning to Umno) You have signed up to contest to be a delegate. What
do you plan to do at the Umno general assembly?
I'll go and sit behind. If there is an opportunity to speak, I will speak even (if given) five minutes.
* That is a huge platform (the Umno assembly).
Big platform but talk for five minutes.
* If given the chance to speak, what would you say?
(Laughs) Wait for it. If I tell you now, it won't be fun. (Then) people will not read the newspapers.
* When you were prime minister and Abdullah your deputy, there was a report released regarding the Oil for Food scandal. Many world leaders (were implicated). Pak Lah himself was implicated - his name was listed as a beneficiary. But there was no action taken at that time. Were you aware of this?
When I was PM, I was not aware (of this) ... only after I stepped down was the (UN) report made. What is important is not whether he is a beneficiary or not but as a deputy prime minister - or anyone who holds a (government) position - he should not be involved in any commercial transactions. It looks like he was involved. How far he was involved, I don't know ... but I think there should be an investigation by an independent body, not by those under him. An Indian minister Natwar Singh quit when his name appeared on the list.
* When Pak Lah was asked about it, he denied any knowledge but conceded that
there were businessmen who met him to ask for support (regarding the
programme). Maybe that's why his name was on the list.
That person was his sister-in-law ... that's what I found out. (see translated LIST below, rginal in Arabic, from Iraqi website)
* Were those names from Malaysia listed (in the UN report) genuine?
The genuine ones ... like Effendi (no further details) yes and (another person whose name was not audible) ... but they were not working with the government.
At least, I should have known or (at least) get my permission but no ... no permission was asked, and I didn't know anything about it until I resigned. If it happened during my era as prime minister, I would have rejected it and taken the necessary actions.
* Now it seems the prime minister does not want to answer your questions. He appears not to be paying any attention to you. Will you continue talking?
I will continue talking. If he doesn't answer, don't answer ... because he can't answer...
If he answers, 'it is right what Dr Mahathir said, it is his (Abdullah's) mistake (that) he wants to allow Singapore fighter jets to use Malaysian airspace - is that right or wrong? If he says 'right' then people will be angry at him so he doesn't answer, (keeps) quiet.
But he is using Brendan Pereira (New Straits Times group editor) to dig up Ani Arope (former TNB CEO) and Tajuddin Ramli (former MAS chief). Apparently, I forced Tajuddin Ramli (to buy MAS shares). I can give the statement that he (Tajuddin) was elated to get MAS...
* (Returning to Umno) How are you going to garner support from party members
and the public for your actions?
I felt that I should express this matter (the issues) because it is true. I may not get support because I know Umno members are very afraid of the leadership.
Those who do things which are not approved by the leadership will get a call. They got a call from Perth (when Abdullah was holidaying there), from all over, telling them to stop (this is believed to be made in reference to inviting him to speak at Umno meetings), and the few that are brave have objected.
If this is what Umno wants, to hold on to people who do wrongs, and if you don't want to take (Umno) back from him, this is what you have to accept. People get the government they want and if people can accept a leader that I say is a dictator, who does not allow me to talk to Umno... I was Umno president for 22 years. I was free to talk to Umno members. He was also free to talk to Umno members. Now I am being told that I cannot talk to Umno - Umno members cannot invite Dr Mahathir.
I know the Umno supreme council has decided that I cannot talk to Umno but Abdullah made the statement that Umno was free to invite whoever they want ... but in reality, they are not free because they will be called and told to cancel it. Look at Perlis (where the Umno Padang Besar division cancelled its invitation to Mahathir).
* You say you want to strengthen the unity in Umno but what is happening now
will lead to an internal crisis.
When Tunku Abdul Rahman did not do something, there were problems... Umno belongs to the people and has to fulfill their aspirations.
* There is a perception that Umno people must respect and defend the leadership. What is your view on this?
Even in Islam (during prayers) if the imam does not recite properly, it is our duty to correct (him) ... even Saidina Abu Bakar (one of the caliphs) said, if I make a mistake, correct me... Can't I even reprimand a human being? I am only reprimanding...
* What is being questioned is the way in which you reprimand - from the outside (publicly) and it is embarrassing to the party president and prime minister.
Even back then, I reprimanded Tunku Abdul Rahman but Umno remained. He realised it and he withdrew ... Datuk Onn also realised it and he too withdrew, but this goes to the extent of not letting people talk, closing their mouths, (getting) angry with ministers... I have never seen things like this. That's why I have to say things a bit harsh. If I whisper, I know nothing will happen.
* Another issue is the quota system in Umno (which requires a minimum number of nominations to contest the top posts in the party). Do you think it should be continued?
There are times when it is needed, when faced with a particular problem. We don't want a split, it is needed, but not something permanent.
____
Dr M: I did not shackle the judiciary
http://www.malaysiakini.com/news/55832
Govt will not reverse decision on bridge
http://www.malaysiakini.com/news/55843
Petronas' accounts a secret due to us
http://www.malaysiakini.com/letters/55834
Why Petronas' accounts are secret.
http://www.malaysiakini.com/letters/55721
The Background to Oil-for-Food Scandal.
Saturday, October 29, 2005, from Msiakini
M'sia PM's relatives linked to oil-for-food scandal
Malaysian Prime Minister Abdullah Ahmad Badawi has been cleared of involvement in the Iraq oil-for-food scandal, but a United Nations inquiry has implicated two of his relatives, reports said on Saturday.
Malaysiakini identified the two as Mr Faek Ahmad Shareef, an Iraqi immigrant who was married to Datuk Seri Abdullah's sister-in-law but later divorced, and Ms Noorasiah Mahmood, the sister of Abdullah's late wife who died this month.
According to the report, Mastek made the single largest payment among 2,200 companies from 66 countries which were found to have paid bribes in the United Nations inquiry unveiled this week.
The New Straits Times did not name Ms Noorasiah, but did identify Mr Faek although not as a relative of the prime minister.
The daily also cited the UN report as saying there was no evidence that Datuk Seri Abdullah had benefited from the oil-for-food programme. He was named last year as being among Malaysians who had received benefits from Saddam under the programme.
Mr Faek told the newspaper that trading the oil allocations was 'just a business' and that it had been conducted 'under UN supervision'.
'There is some truth in the report but it is not the whole truth,' he was quoted as saying. 'I helped Iraqis when millions of people were dying because of the sanctions.'
The international inquiry committee, led by former US central bank chief Paul Volcker, spent 18 months examining what went wrong with the UN oil-for-food programme that ran from 1996 to 2003. -- AFP
Sunday, October 30, 2005, also from Msiakini
Report: Nearly half those involved in oil-for-food program were corrupt
The Associated Press; Oil-for-food Websites
In a scathing final report documenting massive corruption in the U.N. oil-for-food program, investigators Thursday accused more than 2,200 companies, and prominent politicians, of colluding with Saddam Hussein's regime to bilk the humanitarian operation of $1.8 billion.
The 623-page document exposed the global scope of a scam that allegedly involved such name-brand companies as DaimlerChrysler and Siemens AG, as well as a former French U.N. ambassador, a firebrand British politician and the president of Italy's Lombardi region.
It meticulously detailed how the $64 billion program became a cash cow for Saddam and more than half the companies participating in oil-for-food -- at the expense of Iraqis suffering under U.N. sanctions. It blamed shoddy U.N. management and the world's most powerful nations for allowing the corruption to go on for years.
"What I do want to emphasize is that the corruption of the program by Saddam ... could not have been nearly so pervasive had there been more disciplined management by the U.N. and its agencies," said Paul Volcker, a former Federal Reserve chairman who led the investigation.
Volcker and many nations said the report underscored the urgent need to reform the United Nations. Earlier reports in his investigation have already led to criminal inquiries and indictments in the United States, France, and Switzerland. Volcker said his team would cooperate with legal authorities following up on the report.
The investigators found that companies and individuals from 66 countries paid illegal kickbacks using a variety of methods, and those paying illegal oil surcharges came from, or were registered in, 40 countries.
The companies came from Thailand, Malaysia, Russia, Belarus, Syria, Canada and many other places. Many businesses in the developing world made large payments to get humanitarian contracts.
[Malaysia: (LIST EXTRACTED FROM THE TRANSLATED LIST);
1-Fayiq Ahmad Sharif/ 12.5 million
2-Betmal Co./ 4 million
3-Tade pepper/ 4 million
4-Mastik/Fayiq Ahmad Sharif/ 57 million
5-Hawala/ 7 million
Million refers to millions barrels of oil, who are the others in 2,3 & 5??]
Vietnam Northern Food Corp. purportedly paid $37.5 million in kickbacks, while Egypt's Holding Company for Food Industries allegedly paid $30.5 million.
Asked what the report said about the state of global business, Volcker said: "There's a lot of corruption in the world."
Most of the contracts went to Russian and French companies and individuals, who were rewarded for their governments' outspoken opposition to the sanctions. But even firms in countries supportive of the sanctions, such as the United States, found ways to manipulate the system illegally, sometimes by using Russian firms as middlemen.
The oil-for-food program, which ran from 1996-2003, allowed Iraq to sell limited and then unlimited quantities of oil provided most of the money went to buy humanitarian goods. It was launched to help ordinary Iraqis cope with U.N. sanctions imposed after Saddam's 1990 invasion of Kuwait.
But Saddam, who could choose the buyers of Iraqi oil and the sellers of humanitarian goods, corrupted the program by awarding contracts to - and getting kickbacks from - favored buyers.
Volcker's $38 million investigation, which ran for more than a year, had earlier faulted U.N. Secretary-General Kofi Annan, his deputy, and the Security Council for tolerating corruption.
Thursday's report detailed just how companies bilked the program: through surcharges paid for humanitarian contracts for supplies; and via kickbacks for oil contracts. Most of the illicit income -- more than $1.5 billion -- came from the humanitarian contracts.
Among the companies that paid illegal surcharges were South Korea's Daewoo International and three subsidiaries of Siemens AG of Germany, as well as the Brussels, Belgium-based Volvo Construction Equipment.
On the oil side, contractors listed included Texas-based Bayoil and Coastal Corp., Russian oil giant Gazprom, and Lukoil Asia Pacific, a subsidiary of the Russian company Lukoil.
The founder and former chairman of Coastal, Texas oil tycoon Oscar Wyatt, pleaded not guilty Thursday in New York to charges that he conspired to pay several million dollars in illegal kickbacks to Saddam's regime to win contracts through the program.
His trial date was set for June 20.
Volcker's report referred to Wyatt, 81, as a "longtime and loyal oil customer of Iraq," the lone exception to an Iraqi ban on selling oil to American companies.
Among the individuals targeted in the report, investigators found that Jean-Bernard Merrimee, France's former U.N. ambassador, received $165,725 in commissions from oil allocations awarded to him by the Iraqi regime. He is now under investigation in France.
Merrimee "began receiving oil allocations that would ultimately total approximately 6 million barrels from the government of Iraq," the report said. He has denied wrongdoing.
Other "political beneficiaries" included British lawmaker George Galloway; Roberto Formigoni, the president of the Lombardi region in Italy; and the Rev. Jean-Marie Benjamin, a priest who once worked as an assistant to the Vatican secretary of state and opposed Iraqi sanctions.
Formigoni, in a statement, said he received "neither a drop of oil, nor a single cent." Galloway also denied the allegations, saying "I've never had a penny through oil deals and no one has produced a shred of evidence that I have." Benjamin has also denied any personal benefit from the program.
The report strongly criticizes the U.N. Secretariat and Security Council for failing to monitor the program and allowing the emergence of front companies and international trading concerns prepared to make illegal payments.
In a letter to Annan, the committee said its task had been to find mismanagement and evidence of corruption, and "unhappily, both were found and have been documented in great detail."
Yet the report cleared former U.N. Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali, who headed the world body when the oil-for-food program was launched, of accepting bribes. Volcker had earlier raised suspicion about the extent of his involvement.
The letter said responsibility should start with the U.N. Security Council, which is dominated by its five permanent members: Britain, China, France, Russia and the United States. "It was, as one past member of the council put it, a compact with the devil, and the devil had means of manipulating the program to his ends."
The United States said the report again showed the need for urgent reform of the United Nations.
"I do think it does highlight that there are certain management practices within the U.N. that need reform," State Department spokesman Sean McCormack said. "We're going to continue to urge and push for management reform at the United Nations.
In the report, Volcker's team gave several examples of just how companies and Saddam went about manipulating the program. German car manufacturer DaimlerChrysler's dealings were emblematic on a small scale.
According to Volcker's team, DaimlerChrysler had oil-for-food contracts worth about $5.2 million to sell Iraq spare parts and vehicles. The contracts were paid out of a U.N. bank account funded by Iraqi oil sales, also administered by the U.N.
One of those contracts was to sell Iraq's Oil Ministry a Mercedes armored van worth about $70,000. As a sweetener, a DaimlerChrysler agent signed a secret deal to give Iraq a $7,000 kickback -- 10 percent of the van's value.
When the final contract for the van was submitted for U.N. approval, the price of the truck was inflated to include that amount. That meant that the U.N. fund ended up paying DaimlerChrysler for the kickback.
DaimlerChrysler said it was aware of the report but declined to comment because of ongoing investigations by the Securities and Exchange Commission and the Justice Department.
Synopsis "Printed for the use of the Committee on Governmental Affairs."
Related information; Bibliographic information
Title: How Saddam Hussein Abused the United Nations Oil-for-Food Program
ISBN: 0160745721 Publisher: For sale by the Supt. of Docs., U.S. G.P.O
Author(s): United States. Congress. Senate. Committee on Governmental Affairs. Permanent Subcommittee on Investigations
Publication Date: 2005 ; Pages: 212
April 27, 2004; About the Oil-for-Food Scandal
After the 1991 Gulf War, the U.N. imposed economic sanctions on Saddam's regime. Concerned that the sanctions were hurting the people of Iraq, in 1996 the Security Council established the Iraq Oil-for-Food Program (OFP). Under strict U.N. control, Iraq would be allowed to export oil and import food and humanitarian supplies.
Over time, the program grew. Over seven years, $65 billion worth of oil was sold through the program and $38 billion of goods was imported into Saddam-controlled Iraq. Inspectors, monitors, and local bureaucrats oversaw oil sales, imports, and distribution of the humanitarian aid. The other $27 billion went to Kuwaiti war reparations, to the UN for administrative costs, and to Kurdish-controlled Iraq.
Saddam evaded and abused the sanctions program as much as possible. He smuggled oil out of Iraq. He demanded kickbacks from both sides of the OFP: purchasers of oil and suppliers of goods. The GAO estimates that he earned $10 billion from smuggling ($5.7Bn) and kickbacks ($4.4Bn).
For years before the 2003 Iraq War, much of this was known, and ignored by the U.N. and the U.S. Indeed, there was constant global pressure to abandon or ease the sanctions; various Security Council Resolutions increased the amount of oil that could be sold and broadened the list of goods that could be imported. In 2001, the OFP did tighten up the oil pricing policy, and thus reduced the margin on the kickbacks required from oil purchasers.
Various U.S. agencies reported on the graft and kickbacks throughout 2002 and 2003, with modest attention. The lid blew off the OFP scandal on January 30, 2004, with the publication in Al-Mada, a Baghdad newspaper, of a list of 270 alleged recipients of oil allocations from Saddam. Reportedly the recipients of these vouchers had the right to buy Iraqi oil and could then re-sell it at a tidy profit. The names included oil companies, small trading companies, politicians (many of them vocally pro-Saddam), and at least one U.N. official, Benon Sevan, the head of OFP. (By my estimate, the published list of oil vouchers, in total, was worth about $800 million, one part of the puzzle, NOT the whole thing.)
Whether the list is fraudulent or legitimate, since February, pressure has built for investigations. The UN, the U.S. Congress, and Iraq's Governing Council have all started investigations
Why is the OFP Scandal Important?
It is not just about which bureaucrat had his hand in the till. Nor is it just about which company slipped a dictator a few (or many) bucks.
It is about the UN and its legitimacy. During the run-up to the Iraq war, George Bush's opponents accused him of many misdeeds. Chief among them was "going to war without the UN." But if, the UN was, in fact, Saddam's enabler, if the UN Secretariat was effectively on Saddam's payroll, if important people in major antiwar countries were likewise beholden to the Iraqi regime, then that casts a wholly different light on "unilateralism."
And that is precisely why so many people, on both sides of the global debate, weigh in strongly on the Oil-for-Food scandal.
I highly recommend Claudia Rossett's excellent summary of the issue. It is lengthy, but well worth your while, if you want to understand this issue.
This website, by design, covers many details and news reports. In addition to Ms. Rosett's article, I am working on ways to summarize and present this very complex scandal in useful and accessible ways. Your comments and suggestions toward that goal are appreciated.
Posted by Stephen at April 27, 2004 08:22 PM
This entry was posted in the following categories: News Reports/General
Comments
Thanks so much for getting this information out. I have been following Claudia Rossett's articles; she's tenacious! Keep up the good work.
from
http://healingiraq.blogspot.com/
The mother of all scandals
Tim Blair brought this to my attention yesterday and I dug up the list of companies, politicians, and organizations from 51 countries that had received bribes in oil from the former regime in return for their 'services' in defending the regime and opposing the US campaign against him.
These shady deals were all done under the auspices of the UN and the Oil for Food program. The bribes add up to a total of 3.3 billion barrels of Iraqi crude oil (worth over 70 billion dollars). Here is the translated list. And here the original in Arabic.
Now you know why Iraqis suffered from the UN sanctions. Now you know why hundreds of thousands of Iraqi children had to die during the last ten years. Now you know why those people were vehemently anti-war.
The list was published in Al-Mada, an independent Iraqi newspaper, it was leaked from the Ministry of Oil archives. There may be a few errors in my translation, so if you can find any of these please point them out to me so I can make the proper corrections.
Here are some links on the story. From Reuters, commercial appeal, New York post, and the Seattle Post. Sam also posted about it here.
# posted by Zeyad : 1/29/2004 07:47:23 PM
comments (136)
http://hammorabi.blogspot.com/
The Scandal is Bigger!
What leaked to the media from the oil bribes list submitted to the Iraqi GC by the ministry of oil is just the surface of the tip of the iceberg. Hoshiar Zibari the foreign minister indicated during his visit to Bulgaria that the bribes list is true.
Indeed bribing was a policy that Saddam's regime used to depend on for long time since its control of power. In 1970s and 1980s when VIP individuals visit the country, the Iraqis used to whisper, how much they took!
In actual fact dependent sources said that the published list is just the tip of the iceberg. The real list contains hundreds of names of very VIPs individuals. Among them are Arab politicians, artists, actors and writers. There are sons of heads of states and top governmental officials.
One female actor received bribes at many occasions. In only one of these occasions she received 5 Millions US Dollars! This may be Raghdah a Syrian actor lives in Egypt who used to go with a group of MPs, actors, journalist and others so often regularly in a propaganda of breaking the sanction. At least once she met Saddam publicly!
There is another story leaked to the media about an Arab attractive young singer, she received more than 1.5 Millions Dollars for spending 3 nights with Udy Saddam's eldest son!

(One of the parties Saddam son used to do during the sanction!)
In 1983-1985 Saddam's regime bought 128 top class apartments in Al Jizah which is a top class area in Cairo and gave them as a bribery gifts to its supporters.
Those published in the list either kept silent or denied it or telling that they were doing trades! We really so surprised how can a journalist or MP or politician or actor or a son of an official turn in one night into an oil dealer!
We would like to know the rest of the list and about the results of the investigations. These are true documents and not conspiracy. Indeed those who tried to put doubts on it are directly or indirectly defending the ugly act of a tyrant regime.
Saddam bribed too many people by different ways for long time to keep them silent about the parties of executions like the one below!
(one of the regular executions he used to do in the cities during his reign.



The Scandal of Oil Bribes!
(Update List Below)
Documents found in the ministry of oil indicates that Iraqi oil worth hundred of millions of dollars have been given as bribes to Arabs and non Arabs individuals including politicians, MPs, Journalists, Parties, companies, and others in return for Saddam propaganda. The Iraqi ministry of oil said it will follow them through the appropriate lawful procedures and the International police.
Almada Iraqi newspaper and other Iraqi sites have published the names of 270 individuals from 50 countries including 16 Arab states. The deals were signed by SOMO which is an Iraqi oil company owned by the cousin of Saddam.
All the companies are Non-end users which mean they do not own refineries and acted as intermediary agents to sale their bribes!
I was unable to do a correct translation of the names but here is the list in Arabic published by the Iraqi Parliament site. The numbers beside each name represent millions of barrels of oil given.
Many sources think that the list is only the iceberg of bribes given over 35 years but the list above is given over the last few years from the oil for food or as smuggling of oil outside the UN programme. These individuals should be followed up not only by the Iraqis but by the UN to investigate the breach of the UN sanction at that stage! This breach is coin with two faces, one is the breach of sanction and the other is the breach of using the money for propagand or things other than the food for the starved Iraqi children!
List from MEMRI.
List includes:
1.Syria: 14 individuals total 89 millions barrel. Including the son of minister of defence and Hamiadah Naana.
2.Jordan: Ashanfari Group 5 millions
3.Cyprus: more than 33 millions including Mohammad Alhoni editor of AlArab newspaper who got 17 millions! Plus other 2 companies
4.Turkey: 11 individuals with 82.5 millions
5.Vietnam: 4 with 12.2 millions
6.Sudan: 3 with 12 millions
7.Yemen: 3 with 16.3 millions including AbdAlkarem AlAryani
8.Bangladesh: 43 millions for Molana Abd Almanan!!
9.India: 9.5 millions for Beham Sing and congress party!
10.Pakistan: 3 with 23.5 millions
11.Malaysia: 4 with 84.5 millions
12.Indonesia: 6 with 21 millions including daughter of Sokarno!
13.UAE: 8 with 55.2 millions including Essa Nihian, Sultan Nihian from the ruling family and M Saed Eutiaba
14.Morocco: 3 with 7.4 millions
15.Algeria: 2 for 12 millions
16.Tunisia: 3 for 14.4 millions
17.Italy: 8 for 61.5 millions including church priest and companies
18.Spain: 3 for 36.1 millions
19.Yugoslavia: 4 for 53.5 millions (Socialist party, Left party, Italian party and Kokostontasha party- if wright translation!)
20.Belarusian: 6 for 39.2 millions including communist and liberal parties and the head of the department of presidency
21.Romania: 2 for 6.5 millions including labour party
22.UK: 2 for 55.5 millions including George Galloway MP and Mujahdeen Khleek the Iranian group.
23.Canada: Arthur Mill Holland for 9.6 millions
24.USA: 2 for 17.5 millions including Shaker Khafaji and Samer Finsent
25.Chad: Foreign minister 3 millions
26.Thailand: the rice trader Gay Born 9.5 millions
27.Panama: one for 11.5 millions
28.Hungaria: 4.7 millions for Hungarian Welfare party
29.South Africa: 4 for 21 millions
30.Philippine: 3.5 millions for Philippine producers
31.Nether land: Cypolt! 3 millions
32.France: 11 for 169 millions including French Arab association
33.China: 5 for 84.1 millions
34.Jordan: 14 for 74 millions including Liath Shibilat, Fakhri Gaawar, Tojan Faisal, Fawaz Ziriakat, Salem Naas, Shaker Bin Zaid, M Saleh Horani, Ziad Yaghmor, Wameth hussien, Mashhor Hadethah, Ziad Ragheb, Salim Naas and ministry of Energy!
35.Palestinians: 6 for 37 millions including PLO and Abo Abas
36.Egypt: 11 for 82 millions including Khaled Jamal Abd Al Naser, Emad Eljalda and other companies
37.Lebanon: 14 for 34 millions including the son of president Lahood
38.Bahrain: 3 companies for 7 millions
39.KSA: 2 companies for 5 millions
40.Qatar: 5 for 24 millions including Mohammad Bin Ali Althani
41.Libya: Shokr Ghanem 1 million
42.Brazil: 2 for 14.5 millions including foad Sarhan
43.Ireland: 2 for 13 millions including Riyadh Altaher
44.Nigeria: 5 for 19.7 millions
45.Kenya: Mohammad Othman for 10.5 millions
46.Bulgaria: 2 for 14 millions including socialist party
47.Austria: 2 for 4 millions including hanz Kogglier
48.Swiss: 11 for 81 millions
49.Minemar union: 5 millions for minister of forest
50.Slovakia: 4 millions for communist party
51.Ukraine: 12 for 46 millions including communist parties
52.Russia: the largest. 1 milliard and 366 millions given to the state! And the others are 46 individuals, parties, statesmen, and companies etc, given 1343.5 millions!
April 22, 2004; Claudia Rosett's Summary
The Oil-for-Food Scam: What Did Kofi Annan Know, and When Did He Know It?
This lengthy article is the best overview of the whole rotten, complicated mess that was the OFP that I have found. If you only read one thing about this story, Ms. Rosett's article is the one thing. It requires 10-15 minutes, but is far more enlightening than futilely Googling the topic for that same amount of time.
The OFP scandal goes far beyond the infamous 270 names and its implications threaten the whole current operation and leadership of the United Nations. In Ms. Rosett's words:
"What lies at the core of this story is the United Nations, and how it came to pass that an institution charged with bringing peace and probity to the world should have offered itself up—willingly, even eagerly—as the vehicle for a festival of abuse and fraud. "
(Contrary to my usual practice of excerpting only, I have taken the questionable liberty of providing the whole document, so important is the information.)
Claudia Rosett (COMPLETE DOC) - a long read..
For years, the United Nations Oil-for-Food program was just one more blip on the multilateral landscape: a relief program for Iraq, a way to feed hungry children in a far-off land until the world had settled its quarrels with Saddam Hussein. Last May, after the fall of Saddam, the UN Security Council voted to lift sanctions on Iraq, end Oil-for-Food later in the year, and turn over any remaining business to the U.S.-led authority in Baghdad. On November 20, with some ceremony, UN Secretary-General Kofi Annan lauded the program’s many accomplishments, praising in particular its long-serving executive director, Benon Sevan. The next day, Oil-for-Food came to an end.
But it has not ended. Suddenly, Oil-for-Food is with us again, this time splashed all over the news as the subject of scandal at the UN: bribes, kickbacks, fraud, smuggling; stories of graft involving tens of billions of dollars and countless barrels of oil, and implicating big business and high officials in dozens of countries; allegations that the head of the program himself was on the take. In February, having at first denied any wrongdoing, Sevan stopped giving interviews and was then reported to be on vacation, heading into retirement. By March, the U.S. Congress was preparing to hold hearings into Oil-for-Food. Kofi Annan, having denied any knowledge of misdeeds by UN staff, finally bowed to demands for an independent inquiry into the UN program, saying, "I don’t think we need to have our reputation impugned."
The tale has been all very interesting, and all very complicated. For those who look yearningly to the UN for answers to the world’s problems, it has provoked, perhaps, some introspection about the pardonable corruption that threatens even the most selfless undertakings. For those who believe the UN can do nothing right, Oil-for-Food, whatever it was about, is a delicious vindication that everyone and everything at the world organization is crooked, the institution a fiasco, and politicians who support it fit for recall at the next electoral opportunity.
The excitement may be justified, but a number of important facts and conclusions have gone missing. Oil-for-Food, run by the UN from 1996 to 2003, did, in fact, deliver some limited relief to Iraqis. It also evolved into not only the biggest but the most extravagant, hypocritical, and blatantly perverse relief program ever administered by the UN. But Oil-for-Food is not simply a saga of one UN program gone wrong. It is also the tale of a systematic failure on the part of what is grandly called the international community.
Oil-for-Food tainted almost everything it touched. It was such a kaleidoscope of corruption as to defy easy summary, let alone concentration on the main issues. But let us try.
Oil-for-Food had its beginnings in the UN sanctions imposed on Iraq following Saddam Hussein’s August 1990 invasion of Kuwait. These prohibited UN member states from trading with Iraq until the regime had satisfactorily disarmed. Saddam refused to comply, and in the aftermath of the first Gulf war the sanctions remained in place. (Even under sanctions, Iraqis were theoretically allowed to import essential foods and medicines, but Saddam’s repressive system prevented them from earning the necessary foreign exchange.) Reports fed by Saddam’s regime soon began to surface that the sanctions were imposing severe suffering on ordinary Iraqis. The UN, then led by Secretary-General Javier Perez de Cuellar, broached the idea of allowing Iraq to sell oil in limited quantities, strictly to buy relief supplies.
At first, Saddam resisted this, too. But in the mid-1990’s, perhaps because he was feeling the pinch, or quite likely because he had by then seen ways and built up the leverage to turn such a plan to his advantage, he finally agreed. On April 14, 1995, the UN (then under Boutros Boutros-Ghali) passed Resolution 986, authorizing as a "temporary measure" what become known as the Oil-for-Food program, and then spent months working out with Saddam the details of implementation.
From the start, the program was poorly designed. Saddam had blamed the fate of starving Iraqi children on the sanctions regime and specifically on the United States. Seeking to address these charges, the Clinton administration went looking for a compromise; with the Secretariat in the lead, the Security Council agreed to conditions on Oil-for-Food that were, to say the least, amenable to manipulation. Saddam, the author of the miseries of Iraq, was given the right to negotiate his own contracts to sell Iraqi oil and to choose his own foreign customers. He was also allowed to draw up the shopping lists of humanitarian supplies—the "distribution plans"—and to strike his own deals for these goods, picking his foreign suppliers. The UN also granted Saddam a say in the choice of the bank that would mainly handle the funds and issue the letters of credit to pay these suppliers; the designated institution was a French bank now known as BNP Paribas.1
To be sure, the UN reserved for itself the authority to reject Saddam’s proposed contracts and his plans for distribution of goods inside Iraq; to control the program’s bank accounts; and to ensure that Saddam’s buying and selling were in compliance with the UN’s humanitarian plan. As spelled out in Resolution 986, oil was to be sold "at fair-market value," and the proceeds were to pay solely for goods and services that would be used "for equitable distribution of humanitarian relief to all segments of the Iraqi population throughout the country."
To all this, the UN added another twist. Unlike most of its relief programs, in which both the cost of the relief itself and UN overhead were paid for by contributions from member states, Oil-for-Food would in every respect be funded entirely out of Saddam’s oil revenues. The UN Secretariat would collect a 2.2-percent commission on every barrel of Iraqi oil sold, plus 0.8 percent to pay for UN weapons inspections in Iraq.
If the aim of this provision was to make Saddam bear the cost of his own obstinacy, the effect was to create a situation in which the UN Secretariat was paid handsomely, on commission, by Saddam—to supervise Saddam. And the bigger Oil-for-Food got, the bigger the fees collected by Annan’s office. Over the seven years of the program, oil sales ultimately totaled some $65 billion. On the spending side, the UN says $46 billion went for aid to Iraq, and $18.2 billion was paid out as compensation to victims of Saddam’s 1990-91 occupation of Kuwait. As for commissions to the Secretariat, these ran to about $1.9 billion, of which $1.4 billion was earmarked for administrative overhead for the humanitarian program (the UN says it turned over $300 million of this to help pay for relief, but no public accounting has ever been given) and another $500 million or so for weapons inspections in Iraq. Discrepancies in these numbers can be chalked up to interest paid on some of the funds, exchange-rate fluctuations, or simply the murk in which most of the Oil-for-Food transactions remain shrouded to this day.
Whether Saddam should have enjoyed the right to dispose of all Iraqi oil was never questioned. In Iraq, oil was the province of a state monopoly, which Saddam in effect claimed for his own, and on that basis was the UN deal struck. The arrangement actually helped strengthen Saddam’s chokehold at home. With sanctions effectively forbidding all other foreign commerce, Iraq’s only legitimate trade was whatever flowed through Saddam’s ministries under the supervision of the UN program. Thus the UN gave to Saddam the entire import-export franchise for Iraq, taking upon itself the responsibility for ensuring that he would use this arrangement to help Iraq’s 26 million people. The success of the program depended wholly on the UN’s integrity, competence, and willingness to prevent Saddam from subverting the setup to his own benefit.
This was perhaps an impossible brief. But the Secretariat eagerly shouldered the burden, accepting along with it the commissions that flowed straight from Iraq’s oil spigots. Introduced as an ad-hoc deal, Oil-for-Food soon took on the marks of a more permanent arrangement. It was a project in which Annan had a direct hand from the beginning. As Under-Secretary General, he had led the first UN team to negotiate with Saddam over the terms of the sales under Oil-for-Food. The first shipment went out in December 1996; the following month, Annan succeeded Boutros-Ghali as Secretary-General.
Nine months later, in October 1997, Annan tapped Benon Sevan, an Armenian Cypriot and longtime UN official, to consolidate and run the various aspects of the Iraq relief operation under a newly established agency called the Office of the Iraq Program (but usually referred to simply as Oil-for-Food). Sevan served as executive director for the duration, reporting directly to Annan. The program was divided into roughly six-month phases; at the start of each phase, Sevan would report and Annan would recommend the program’s continuation to the Security Council, signing off directly on Saddam’s "distribution plans."
An issue that would later become important was how, precisely, the responsibilities for executing the program were parceled out between the Security Council—a committee of fifteen member states—and the Secretariat, run by Annan. All of Saddam’s proposed contracts flowed through the Security Council, which doubled as the Iraq "sanctions committee." But in practice, the fifteen member governments were mostly on the watch for so-called dual-use items: goods that might be used to make weapons.
As it turned out, only two of the five permanent, veto-wielding members appear to have done any overseeing at all. These were the UK and the U.S., both of which had almost no direct business with Saddam’s Iraq. The UN representatives of the other three—France, Russia, and China—devoted their energies chiefly to urging expansion of the program and forwarding the paperwork submitted by the many contractors in their respective nations whom Saddam had selected as his buyers and suppliers. As for the ten rotating members of the Security Council, some—like Syria—were among Saddam’s favored trading partners, while most of the others lacked the resources to keep track of the huge volume of business the program soon generated.
If final responsibility lay anywhere at all, it lay with the Secretariat. It was this body that fielded a substantial presence in Iraq (the U.S., apart from weapons inspectors ejected early on, had none), employing at the height of the program some 3,600 Iraqis plus 893 international staff working in Iraq for the nine UN agencies coordinated by the Oil-for-Food office; another 100 or so were employed back in New York. The Secretariat was the keeper of the contract records and the books, and controller of the bank accounts, with sole power to authorize the release of Saddam’s earnings to pay for imports to Iraq. The Secretariat arranged for audits of the program, was the chief interlocutor with Saddam, got paid well for its pains, and disseminated to the public extremely long reports in which most of the critical details of the transactions were not included.
One of the first changes introduced by Sevan was greater secrecy. According to John Fawcett, the co-author of a 70-page report on Saddam’s finances released in 2002 by the Washington-based Coalition for International Justice, the UN had been fairly open about the specifics of Saddam’s contracts during the first year of the program. From about 1998 on, however, it categorized the most germane details as "proprietary"—carefully guarding Saddam’s privacy in his business deals. Thus, there was no disclosure of such basic information as the names of individual contractors or the price, quality, or quantity of goods involved in any given deal—all vital to judging the integrity of contracts.
Instead, the Office of the Iraq Program released long lists representing billions of dollars in business but noting only the date, country of origin, whether or not the contract had been approved for release of funding, and highly generic descriptions of goods. Typical of the level of detail were notations like "electric motor" from France, "adult milk" from Saudi Arabia, "detergent" from Russia, "cable" from China. Who in particular might be profiting, or at what price, was kept confidential. Nor did the UN disclose interest paid on the Oil-for-Food accounts at BNP Paribas or (possibly) other banks, which toward the end of the program held balances of more than $12 billion. Nor did it ever share with the public the details of how the $1.9 billion in commissions flowing from Saddam for aid and arms inspections (the latter were discontinued from late 1998 to late 2002) were spent by the UN Secretariat.
The year 1998, the first full year of the program under Sevan’s directorship, is of special interest in this connection. For starters, if evidence cited in the Wall Street Journal turns out to be correct, this was the year in which Saddam’s government may have begun covertly sending gifts of oil to Sevan himself by way of a Panamanian firm. It was also the year in which the UN terminated a contract with a UK-based firm, Lloyd’s Register, for the crucial job of inspecting all Oil-for-Food shipments into Iraq, and replaced it with a Swiss-based firm, Cotecna Inspections, with ties to Kofi Annan’s son Kojo. At the time, neither Cotecna nor the UN declared these ties as a possible conflict of interest, which they were.2
Also in 1998, at Sevan’s urging, the UN expanded Oil-for-Food to allow Saddam to import not just food and medicine but oil-industry equipment, and at Annan’s urging more than doubled the amount of oil Iraq was allowed to sell, raising the cap from roughly $4 billion to more than $10 billion per year. That same year, after much hindering and dickering, Saddam threw out the UN weapons inspectors—forbidding their return until the U.S. and Britain finally forced the issue four years later.
This brings us to 1999-2000, when, following Sevan’s urging, the program expanded yet further; with more funds devoted to the oil sector, and with the weapons inspectors gone, the UN now removed the limits on sales. In 2000, Saddam enjoyed a blockbuster year. By this time he was not only selling vastly more oil but had institutionalized a system for pocketing cash on the side.
It worked like this. Saddam would sell at below-market prices to his hand-picked customers—the Russians and the French were special favorites—and they could then sell the oil to third parties at a fat profit. Part of this profit they would keep, part they would kick back to Saddam as a "surcharge," paid into bank accounts outside the UN program, in violation of UN sanctions.
By means of this scam, Saddam’s regime ultimately skimmed off for itself billions of dollars in proceeds that were supposed to have been spent on relief for the Iraqi people. When the scheme was reported in the international press—in November 2000, for example, Reuters carried a long dispatch about Saddam’s demands for a 50-cent premium over official UN prices on every barrel of Iraqi oil—the UN haggled with Saddam but did not stop it.
Beyond that, Saddam had also begun smuggling out oil through Turkey, Jordan, and Syria. This was in flagrant defiance of UN sanctions and made a complete mockery of Oil-for-Food, whose whole point was to channel all of Saddam’s trade. The smuggling, too, was widely reported in the press—and shrugged off by the UN. In the same period, Saddam imposed his own version of sanctions on the U.S., demanding that Oil-for-Food funds be switched from dollars into euros. The UN complied, thereby making it even harder for observers to keep track of its largely secretive and confusing bookkeeping.
As Oil-for-Food grew in size and scope, the U.S. mission to the UN began putting a significant number of its relief contracts on hold for closer scrutiny. Both Sevan and Annan complained publicly and often about these delays, describing them as injurious to the people of Iraq and urging the Security Council to push the contracts through faster. What Sevan did not convey was that, by 2000, complaints had begun reaching him about Iraqi government demands for kickbacks from suppliers on the relief side. These (according to a recent report in the Financial Times) Sevan simply buried, telling complainants to submit formal documents to the Security Council through their countries’ UN missions (something they had no incentive to do since Saddam would most likely have responded by scrapping the deals altogether).
By 2002, the sixth year of the program, it was no longer credible that the UN Secretariat could be clueless about Saddam’s systematic violations and exploitation of the humanitarian purpose of Oil-for-Food. On May 2, in a front-page story by Alix M. Freedman and Steve Stecklow, the Wall Street Journal documented in detail Saddam’s illicit kickbacks on underpriced oil contracts, noting that "at least until recently, the UN has given Iraq surprising influence over the official price of its oil." In fact, against the resistance of Russia, France, China, and the UN Secretariat, the U.S. and Britain had been trying to put a halt to the kickbacks through an elaborate system to enforce fairer pricing—but with only limited success. Sevan, clearly aware of the scam, was quoted in the Journal article as saying he had "no mandate" to stop it.
Apparently, however, there was a near-boundless mandate for the Secretariat to expand the scope of the spending. A mere fortnight later, on May 14, 2002, the Security Council passed a resolution cutting itself out of the loop entirely on all Oil-for-Food contracts deemed humanitarian, and giving direct power of approval to the Secretary-General. Henceforth, the Security Council would confine its oversight to items of potential dual use, such as chemical spraying equipment, or forbidden goods like highly enriched uranium, nuclear-reactor components, and the like. Unimpeded responsibility for the "humanitarian" aspect of the program fell to Annan.
The next month, "humanitarian" became a broad category indeed. On June 2, Annan approved a newly expanded shopping list by Saddam that the Secretariat dubbed "Oil-for-Food Plus." This added ten new sectors to be funded by the program, including "labor and social affairs," "information," "justice," and "sports." Either the Secretary-General had failed to notice or he did not care that none of these had anything to do with the equitable distribution of relief. By contrast, they had everything to do with the running of Saddam’s totalitarian state. "Labor," "information," and "justice" were the realms of Baathist party patronage, propaganda, censorship, secret police, rape rooms, and mass graves. As for sports, that was the favorite arena of Saddam’s sadistic son Uday, already infamous for torturing Iraqi athletes.
Then came the autumn of 2002, when President Bush delivered his warning to Saddam to comply with sixteen previous UN resolutions to disarm, and the U.S. persuaded the Security Council to pass a seventeenth. Though there was by this time no dearth of damning information in the public domain, Oil-for-Food rolled on. On September 18, the Coalition for International Justice released its heavily researched report, Sources of Revenue for Saddam & Sons, documenting rampant corruption and smuggling under UN sanctions and Oil-for-Food, warning of an Iraqi shift from "informal, on-the-sly deals" to increasingly "brazen and formal government-to-government arrangements," and asking how, "given . . . the world’s largest humanitarian program ever, can there remain shortages of basic medicines and foodstuffs" in Iraq? Four months later, with Saddam still defiant and war looking likely, Annan signed a letter to the Security Council in which, among other things, he approved the use of $20 million in Oil-for-Food funds to pay for an "Olympic sport city" and $50 million to equip Saddam’s propaganda arm, the Ministry of Information.3
By then, of course, debate over Iraq was raging in the Security Council, and the U.S. and Britain were bitterly at odds with France and Russia. Annan weighed in publicly on the side of the latter, urging yet more time and tolerance. He did not mention his own interest as the boss of a massive relief program funded by Saddam. Neither did he mention that Saddam’s commercial deals heavily favored French and Russian companies, though he had access to actual numbers about those deals that, thanks to UN secretiveness, the public did not.
On March 17, with the U.S.-led coalition poised to invade, Annan pulled his international staff out of Iraq. Three days later, as coalition forces rolled into Iraq, he expressed regret that war had come "despite the best efforts of the international community and the United Nations." Describing the UN as the keeper of international "legitimacy," he assured the Iraqi people that, as soon as possible, the UN would be back to do "whatever it can to bring them assistance and support."
Following the fall of Saddam’s regime, the U.S.-led coalition decided that Iraq had experienced enough of UN-style "assistance and support," at least as far as Oil-for-Food was concerned. With Russia and France suddenly willing to go along, perhaps to avoid scrutiny of Oil-for-Russia and Oil-for-France, the Security Council voted unanimously on May 22 that the program should be wound down. No more oil revenues were to flow in, but the UN Secretariat was to continue administering the remaining relief contracts until November, when any unfinished business would be turned over to the Coalition Provisional Authority (CPA) in Baghdad.
At that stage, Oil-for-Food had close to $13 billion in BNP Paribas’s Iraq accounts, most of it set aside to pay for contracts already approved. During the summer and early fall, the New York office began tidying up loose ends, renegotiating, "prioritizing," and basically removing the graft elements from the remaining contracts before handover to the CPA. In these efforts, the UN got some prompting from the U.S. Defense Contract Management Agency (DCMA)—the agency that has been auditing Halliburton’s recent activities in Iraq.
From the thousands of remaining contracts, the DCMA (together with the Defense Contract Audit Agency) culled a batch of 759 of the largest deals, valued altogether at $6.9 billion. The reviewers estimated that among these contracts, almost half were overpriced by about 21 percent, for a total of $656 million that Saddam’s regime had overpaid. This was in all likelihood the kickback component, part of which the suppliers were meant to share illicitly with the regime. Dryly, the DCMA’s report adds that, in the course of its researches, "Some items of questionable utility for the Iraqi people (e.g., Mercedes Benz touring sedans) were identified."
By the time the Oil-for-Food office was finished renegotiating its contracts, it had scrapped more than a quarter of them. Some of the reasons, listed in UN public documents, are intriguing. There was, for example, the Syrian supplier of "spare parts for rotating equipment" whom it was "not possible to contact"; the Lebanese vendor of "welding machines" who was "unwilling to accept the 10-percent deduction"—i.e., a price minus the bribe-plus-kickback; and the Jordanian seller of school furniture whose contract had to be dropped because "company does not exist and the person in charge moved to Egypt."
Then came the formal ceremonies to which I have already alluded. On November 19, Sevan’s office put out a press release praising Oil-for-Food as "one of the most efficient of UN programs." On November 20, Annan chimed in with his own praise for Oil-for-Food, paying tribute to the staff and "particularly to its executive director, Benon Sevan." On November 21, almost seven years after setting up shop as a temporary and limited measure to bring food and medicine to hungry people in Iraq, the program shut down, handing the CPA a royal mess.
Sevan had assured the Security Council that, along with control of the more than $8 billion in funds and contracts still to be administered, the CPA would get "the entire Oil-for-Food database." In fact, the transfer was incomplete. Plenty of contract information was missing. So Byzantine were the BNP Paribas accounts that, rather than risk interrupting relief deliveries, the CPA simply left them under the management of the UN treasurer, who until almost a year after the fall of Saddam never got around to sending any current bank statements, let alone prior records.4
Meanwhile, however, the Iraqi Governing Council had itself begun to pore over records of the Saddam regime from various ministries, and former Baath officials were also starting to talk. On December 5, a British adviser to the Council, Claude Hankes-Drielsma, wrote from Baghdad to Annan, urging the UN to "take the moral high ground" and appoint an independent commission to investigate profiteering under Oil-for-Food.
Not a moment too soon: now the revelations were beginning to flow rapidly. On January 25 of this year, the Iraqi newspaper Al-Mada published a list, reportedly recovered from the Iraqi oil ministry, of some 270 individuals and entities in some 50 countries who were alleged to have received vouchers good for oil from Saddam Hussein. The list was an eye-opener. It included the former French Interior Minister Charles Pasqua, British MP George Galloway, Indonesian President Megawati Sukarnoputri, the Russian nationalist Vladimir Zhirinovsky, a large number of Russian oil companies, the Russian state, and the Russian Orthodox Church. It also included the family name of the head of the UN Oil-for-Food program: Sevan.
Those named in Al-Mada’s list ignored, denied, or dismissed it on grounds that they had legitimately bought oil from Saddam. As for Sevan, he categorically repudiated the notion that he had ever received oil or oil money from the Iraqi regime, while Annan, in a statement more artfully hedged, said: "As far as I know, nobody in the Secretariat has committed any wrongdoing." A spokesman for the UN Secretariat repeated the by-now usual line that Oil-for-Food had been the most audited program at the UN—"audited to death" was the exact phrase—and in late February the Oil-for-Food office released a seven-page statement clearly aimed at deflecting blame for any graft involved with the program.
According to this official account, the Secretariat had no responsibility for confirming that contract-pricing was fair, or that suppliers were legitimate (that was the job of Saddam and the UN country missions); no responsibility for implementing the program (that too was the job of Saddam); no responsibility for either spotting or stopping corruption by Saddam via Oil-for-Food contracts (that was the job of the Security Council); and no awareness of unauthorized oil exports (though the office confirmed its knowledge of "media reports on alleged violations"). By the light of this clarification, indeed, it was hard to tell what the Oil-for-Food program was, in fact, responsible for, beyond controlling the opaque bank accounts, checking that the contracts—honest or not—were properly punctuated, watching Saddam do whatever he chose, and collecting a 2.2-percent commission on his oil.
And so we arrive at the denouement—at least so far. On February 29, the New York Times published a long news article based on "a trove of internal Iraqi government documents and financial records" unearthed by the Iraqi Governing Council. The article described oil traders lugging suitcases full of illicit cash to the ministries and cited stacks of evidence showing that, through Oil-for-Food, Saddam’s regime had squirreled away billions for itself while ordinary Iraqis received expired medicines and substandard rations.
Still the UN hung tough. On March 3, Hankes-Drielsma notified Annan that Iraqi authorities had asked an auditing firm, KPMG International, and a law firm, Freshfields Bruckhaus Deringer, to prepare an independent report. In his letter, Hankes-Drielsma explained his reasoning:
Based on the facts as I know them at the present time, the UN failed in its responsibility to the Iraqi people and the international community at large. The UN should not be surprised that the Iraqi people question the UN’s credibility at this time and any future role for the UN in Iraq. It will not come as a surprise if the Oil-for-Food program turns out to be one of the world’s most disgraceful scams and an example of inadequate control, responsibility, and transparency, providing an opportune vehicle for Saddam Hussein to operate under the UN aegis to continue his reign of terror and oppression.
On March 10 came confirmation that Annan’s son Kojo had held a consultancy with Cotecna right around the time the company won the UN job to inspect goods coming into Iraq. On March 11 came an article in the Wall Street Journal detailing further links between Saddam’s oil largesse and Sevan. The following week came word that Congress would hold hearings on Oil-for-Food. And on March 19, having ignored, stonewalled, and denied, Annan finally conceded that "it is highly possible there has been quite a lot of wrongdoing," and called for an independent inquiry.
As the various audits, investigations, and hearings gear up to delve into the saga of UN involvement in Saddam’s Iraq, we may learn even more about his worldwide net of corruption. With skill, we may locate some of the billions he is believed to have salted away under UN oversight. With luck, we may get to this money ahead of the terrorists with whom he consorted—if they have not gotten to it already. Already known, for example, is that two firms doing business with Saddam through Oil-for-Food were linked to financier Ahmed Idris Nasreddin, now on the UN’s own watchlist of individuals "belonging to or associated with" al Qaeda.
But let us retain our focus. That Saddam Hussein was a monster and a corrupt monster is not news. That he would exploit, for massive personal gain, a humanitarian program meant to relieve the miseries of his countrymen is horrifying but hardly astonishing. Nevertheless, any investigation that confines itself to detailing the abundantly evident corruption of Saddam Hussein will have missed the point.
What lies at the core of this story is the United Nations, and how it came to pass that an institution charged with bringing peace and probity to the world should have offered itself up—willingly, even eagerly—as the vehicle for a festival of abuse and fraud.
To begin with, Oil-for-Food was an enormous venture in central planning, the biggest project of its kind launched in many a decade and one that utterly ignored the lessons about such systems learned at agonizing cost over the past century. The UN Secretariat, in its well-paid arrogance, set out to administer virtually the entire economy of Iraq. Under its eye, all legitimate trading privileges became the franchise of a tyrant who laid first claim to every barrel of oil and every dollar (or euro) of proceeds. How could Oil-for-Food not help consolidate Saddam’s grip on power? Nevertheless, it was with this grand thief of Baghdad that the UN cut its humanitarian deal, chalking in a fat commission for the Secretariat.
Nor did anyone in the UN system so much as lift an eyebrow, even after questions began to be raised. Last November, before the Security Council of the United Nations, the organization’s Secretary-General proclaimed it a splendid achievement that the UN had legitimized a scheme by which 60 percent of Iraq’s population depended entirely on the rationing cards of a totalitarian state. This was an event that should have seized the vaunted international community with horror. Instead, from out of the mouth of the Angolan ambassador who that month was chairing the UN Security Council there issued only unctuous praise for "the exceptionally important role of the program in providing humanitarian assistance to the people of Iraq."
But all that is only prelude. The scope of UN dereliction is much broader, encompassing factors institutional, personal, and, finally, political.
It is true that Oil-for-Food managed to deliver to Iraqis some portion of what it promised. On sales totaling $65 billion, some $46 billion (by Annan’s uncheckable reckoning) went for "humanitarian" spending. Of this amount, an official total of $15 billion worth of food and health supplies—the original rationale for the program—had been received by the time Saddam fell. The actual figure was no doubt considerably less if you factor in the kickbacks and spoiled goods; from the remainder came the equipment for Saddam’s oil monopoly, the construction materials, the TV studio systems, the carpets and air conditioners for the ministries, and all the rest.
But at what cost? Are we supposed to conclude that, in order to deliver this amount of aid, the UN had to approve Saddam’s more than $100 billion worth of largely crooked business, had to look the other way while he skimmed money, bought influence, built palaces, and stashed away billions on the side, at least some of which may now be funding terror in Iraq or beyond?
No, something was at work here other than passive acquiescence. At precisely what moment during the years of Oil-for-Food did the UN Secretariat cross the line from "supervising" Saddam to collaborating with him? With precisely what deed did it enter into collusion? Even setting aside such obvious questions as whether individual UN officials took bribes, did the complicity begin in 1998, when Saddam flexed his muscles by throwing out the weapons inspectors and when Oil-for-Food, instead of leaving along with them, raised the cap on his oil sales? Did it come in 1999, when, even as Saddam’s theft was becoming apparent, the UN scrapped the oil-sales limits altogether? Or in 2000 and 2001, when Sevan dismissed complaints and reports about blatant kickbacks? Did it start in 2002, when Annan, empowered by Oil-for-Food Plus, signed his name to projects for furnishing Saddam with luxury cars, stadiums, and office equipment for his dictatorship? Or did the defining moment arrive in 2003, when Annan, ignoring the immense conflict posed by the fact that his own institution was officially on Saddam’s payroll, lobbied alongside two of Saddam’s other top clients, Russia and France, to preserve his regime? Certainly by the time Annan and Sevan, neck-deep in revelatory press reports and standing indignantly athwart their own secret records, continued to offer to the world their evasions and denials, the balance had definitively tipped.
Annan’s studied bewilderment is itself an indictment not only of his person but of the system he heads. If anyone is going to take the fall for the Oil-for-Food scandal, Sevan seems the likeliest candidate. But it was the UN Secretary-General who compliantly condoned Saddam’s ever-escalating schemes and conditions, and who lobbied to the last to preserve Saddam’s totalitarian regime while the UN Secretariat was swimming in his cash.
Annan has been with the UN for 32 years. He moved up through its ranks; he knows it well. He was there at the creation of Oil-for-Food, he chose the director, he signed the distribution plans, he visited Saddam, he knew plenty about Iraq, and one might assume he read the newspapers. We are left to contemplate a UN system that has engendered a Secretary-General either so dishonest that he should be dismissed or so incompetent that he is truly dangerous—and should be dismissed.
The final perfidy, though, is not personal but political. The UN, in the name of its own lofty principles, and to its rich emolument, actively helped sustain and protect a tyrant whose brutality and repression were the cause of Iraqi deprivation in the first place. What can this mean? The answer may be simply that, along with its secrecy, its massed cadres of bureaucrats beholden to the favor of the man at the top, its almost complete lack of accountability, external oversight, or the most elementary checks and balances, the UN suffers from an endemic affinity with anti-Western despots, and will turn a blind eye to the devil himself in order to keep them in power. Certainly there is much in its history and its behavior to support this view.
Perhaps, then, the complicity was there all along, built in, and was merely reinforced year after year as the UN collected the commissions and processed the funds that transformed Oil-for-Food into the sleaziest program ever to fly the UN flag and the single largest item on every budget of all nine UN agencies involved, plus the Secretariat itself. That, in the end, may be the dirty secret at the center of the Oil-for-Food scandal.
And is this the same United Nations that, now, we are planning to entrust with bringing democracy to Iraq?
Claudia Rosett, who contributes a bi-weekly column on foreign affairs to the Wall Street Journal’s online edition, OpinionJournal.com, is a senior fellow at the Foundation for the Defense of Democracies and an adjunct fellow of the Hudson Institute.
---------------------------------------------
1 As of 2001, one of the largest shareholders in BNP was Iraqi-born Nadhmi Auchi, among Britain’s richest citizens. In the 1980’s Auchi had brokered business deals for Saddam; last year he was convicted in France of illicit profiteering as part of the huge Elf oil scandal. The UN says the Oil-for-Food contract was awarded to BNP on a strictly competitive basis.
2 According to a spokesman at the UN Secretary-General’s office, Kojo Annan had been a trainee at Cotecna from December 1995 to February 1998, and two months later was back at work for the firm as a consultant; his consultancy, which lasted until December 1998, thus coincided with the period during which the UN would have been receiving and reviewing bids for the Oil-for-Food inspection job. Both Kojo and Kofi Annan have denied that Kojo’s consulting work was in any way related to the UN.
3 This is especially significant in light of the role that would be played by Saddam’s televised propaganda during the war. In the event, Saddam may have had to rely on equipment brought in earlier under Oil-for-Food from places like France and Jordan. He was unable to take delivery of TV studio equipment ordered from Russia and approved and funded by the Secretariat on February 7, 2003, just six weeks before the war. But that was not for want of Kofi Annan’s approval.
4 Not only the occupation authority but the Iraqis themselves have failed to penetrate the UN wall of disdain, although it is their own money they wish to know about. The Iraqi Central Bank began requesting copies of the relevant BNP bank statements in July 2003. Not until late March of this year, after I aired the matter in a piece in National Review Online, was there some halting sign of movement in the UN treasurer’s office. Similar stonewalling—no accounting given, no access to statements—has met the repeated efforts of Kurds in northern Iraq to find out what happened to about $4 billion in separate allocations owed to them under Oil-for-Food.
Copyright 2003 Commentary
Posted by Stephen at April 22, 2004 12:03 AM
This entry was posted in the following categories: Opinion/Editorial
GoTo TOP (Main Page)













